
In this article, the author focuses on looking insight into project management planning, by a made-up scenario of the Photos Preservation Project, when doing this unit which is called BSBPMG522 Undertake Project Work in April, May, and June 2021. Each paragraph introduces this project management planning, which is divided into different sections, including
- The project brief,
- The communication plan,
- The risk management and contingency plan,
- Developing a work breakdown structure (WBS),
- Gantt Chart,
- Key milestones,
- Budget allocation & budget analysis and review,
- Recordkeeping, and
- Lessons were learned in this unit.
The Project Brief
| Title of Project | Photos Preservation Project |
| Rationale | To restore and preserve the client’s photos, including making them all digital as a backup, remedial treatment, and rehousing, and helping the client to keep the treasures which can reflect the Victorian historical and social values in ca.1950-1980. |
| Project Team | The author (emerging paper conservator) and XXX (project manager, assuming project manager is the supervisor) |
| Deliverables | Remedial treatment for photos, image digitalisation (backup data in a hard drive and cloud), display and storage packages (framing and storing in enclosures), treatment report including preservation suggestions. |
| Project Sponsor | The client is the sponsor who determines the scope of the project and how far the treatment will go. |
| Estimated Cost | Various (treatment options) |
| Risk | Budget issues, technical issues, OHS issues, HR issues, materials and resource issues, project management failure, external issues, like when in transit. |
| Project librarian (record keeper) and how records will be maintained | The conservator is the project librarian to keep the records in the paper- and digital copies and archives them. |
| Timelines | 2 months |
It is a two-month photos preservation project in the scenario that the author will restore and preserve the client’s photos, including making them all digital as a backup, remedial treatment and rehousing, and helping the client to keep the treasures which can reflect the Victorian historical and social values roughly in 1950 to 1980. Project team, the author is an emerging paper conservator who graduated in 2020 from the cultural materials conservation program, to manage this project and the project should be approved by XXX, the project manager (in here, assuming the supervisor) and the client will also approve the treatment proposal to assist to commence the treatment and project. Deliverables are treated photos, digital images in a hard drive and backup online, display and storage packages, treatment report. Display and storage packages mean some photos need to be framed after treatment as the client’s requirement and the rest of the photos should be packed in a storage standard for home storage. These include an appropriate shipping package with insurance to ensure the deliverables will be sent back to the client. The project Sponsor here is the client who determines the amount of the budget, and the client can choose the treatment options from the suggestions. Estimated cost the author puts various because of the treatment options from the client and because this is a blog post that some details may not be suitable to disclose. Risks in this project, many risks have been identified and details refer to the section of the risk management and contingency plan. Project librarian means the record keeper that the conservator keeps the records and documentation.
The Communication Plan
| Stakeholder/s | Method of Communication | Frequency of Communication | Reason for Communication |
| Client | Phone, face-to-face or virtual meeting, email | Monthly and when the communication if required | Update progress and decision-making from the client due to budget |
| Project Manager | Face-to-face or virtual meeting, email, messenger app from the workplace | Weekly and when the communication if required | Update progress and any changes, and incident report if required |
| The Conservator | Face-to-face or virtual meeting, email, messenger app from the workplace | Weekly and when the communication if required | Any information which the conservator needs to follow up and keep records |
| Artwork Transport (shipping company) | Email, phone call | Be intensive at the final phase of the project | Shipping and insurance |
The Risk Management and Contingency Plan
| Risk | Likelihood of Risk | Consequences | Level of Risk | Contingency |
| External issues like photos being destroyed in transit | Possible | Lose irreplaceable photos, clients being angry/upset which leads to a bad reputation, and reparation if required. | Medium-High | Find an express company with a high reputation, set up a delivery tracking, add insurance, and feedback from the client to confirm the receiving. |
| Budget issues if the client has not enough money for this project | Likely | Affecting the quality of the deliverables, under the expectations from the client, cannot undertake a full restoration, only can-do part of treatment levels. | Medium-High | Seek grants if the client meets the eligibility, scope down the project and treatment levels, and prioritise the photos which need to be restored. |
| OHS issues – Chemical spills | Possible | Severe burns, damage eyesight, and cause harm to the respiratory tract. | Medium-High | Conduct a risk assessment before the treatment, read the MSDS sheet before handling the chemicals, and two people working when dealing with the chemicals. |
| OHS issue – sharp tools like scalpels | Possible | General injuries with blood loss and eye injury. | Medium-High | Not using the sharp tools when hurrying, tired, and improper places, and wearing safety goggles when using a scalpel. |
| OHS issue – Odour organic solvents | Possible | Staff may feel headaches or feel dizzy or nauseous and may cause severe health issues, like cancer. | Medium-High | Adequate ventilation, use fume hood equipment when dealing with odour organic solvents, and wear face masks or respirators. |
| Project management failure | Possible | Loss of profit and reputation, client complaint, loss of trust and relationship from the team, and cannot finish the project in time. | Medium-High | Seek consultation from experts, give flexible timelines, and make sure enough HR resources and materials before commencing the project. |
| Materials and resource issues – out of stock or delaying for shipping | Possible | Cannot finish the project in time, need to spend time waiting for the materials or resource arriving. | Medium-High | Order early when receiving the approval from the client, backup options for purchasing and store basic materials in the workplace. |
| Payment issue if the client does not pay the money | Unlikely | Loss of profit, waste time for treating objects, waste resources. | Medium | Set up a payment plan, pay a deposit to cover the cost of materials, and receive full payment at the same time/before photos are delivered. |
| HR issues such as not enough staff to work on this project | Possible | Cannot finish the project in time as the expectations, overloading work for the staff. | Medium | Reschedule the project timelines and be flexible in time management. |
| Technical issues like the scanner may not work, the computer breaks down, poor Internet that cannot save digital copies to Cloud | Unlikely | May need more time and cost to fix the issue. | Low Medium | Back up scanner and computer and upgrade the data usage plan from the Internet company. |
Ten risks have been identified in this project that the author has listed in the above chart by analysing the likelihood of the risk and level of the risk to figure out the consequences and contingency plan to deal with. The risks involved can come from anywhere in this project and some examples of different areas are:
- Transit (the photos being destroyed in transit),
- Clients (clients not paying/ being able to pay),
- Technical (scanner breaking down, computer issues), and
- OHS issues (chemical spills).
Each risk has been analysed to give an idea for the likelihood of the risk occurring, consequences if they do occur, the severity of the risk in association to the project, and it also allows the author to consider the contingency to prevent the risks occurring.
Most of the risks identified have a level of risk that is medium/high in meaning that there are a lot of things that could prevent this project from being completed entirely. The contingency plans are to prevent these from happening to be able to complete the project. It is essential to do a risk plan as it gives the project planner not only plans to prevent accidents from occurring but also gives the project planner an idea of the budget that needs to be allocated to the contingency plans.
Developing a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
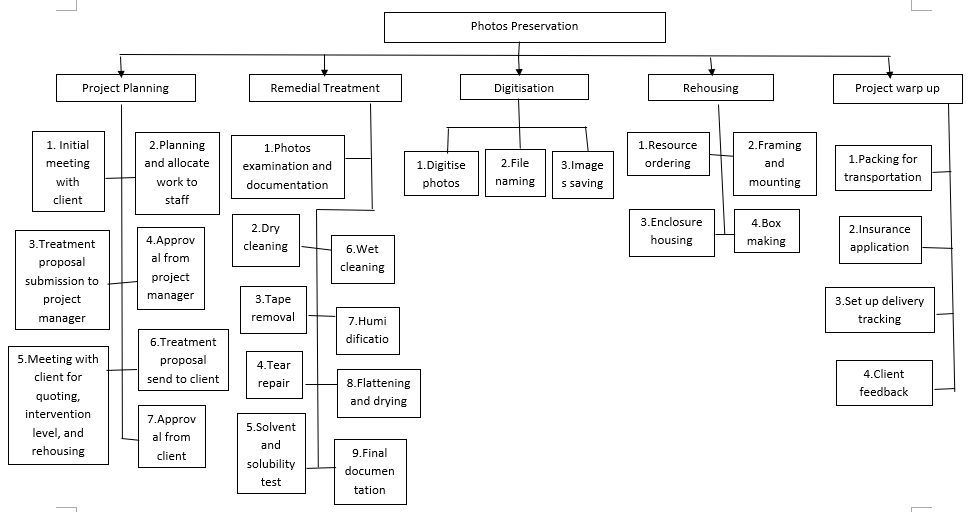
In this diagram of WBS, there are five categories and many tasks to do in this project.
The five categories are:
- Project planning
- Remedial treatment (the treatment options and levels should discuss with the client due to the budgeting)
- Digitisation
- Rehousing
- Project wrap up
All tasks are:
Project planning
- Meeting with the client and understand their needs and expectations (initial meeting)
- Planning and allocating work to staff
- Submit the treatment proposal to the project manager
- Seek approval from the project manager
- A meeting with the client to discuss quoting, treatment intervention level (priorities), and rehousing materials
- Send the treatment proposal to the client
- Waiting for approval from the client
Remedial treatment (Treatment steps vary by the selected option)
- Photo’s examination and documentation (including image taking before treatment and researching the background)
- Dry cleaning
- Tape removal (for certain photos)
- Tear repair
- Solvent and solubility test
- Wet cleaning (for certain photos)
- Humidification
- Flattening and drying
- Documentation (including treatment report, after treatment photography, the recommendation for photography preservation)
Digitisation
- Digitise photos
- File naming
- Save the images to the hard drive and cloud
Rehousing
- Order the suitable size picture frames for framing (for certain photos)
- Framing and mounting
- Store other photos into the enclosures
- Make a box for the entire storage
Project wrap up
- Packing for transportation
- Insurance application
- Set up delivery tracking
- Client feedback
Gantt Chart
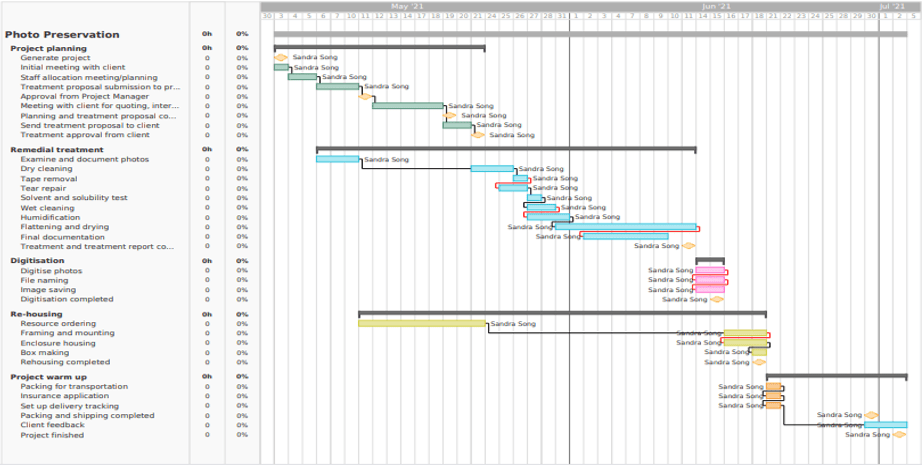
Gantt Chart is a nice tool the author likes to use when dealing with the project timelines. Moving on to the above Gantt chart, as you can see a timeline split into five sub-categories spanning the entire project, the first category in green represents the first three weeks of meeting with the client and organising the future of the project. This can be partially done side by side with the second category Remedial Treatment because by generating a treatment proposal the conservator needs to examine and document the details and address the problem-solving and decision-making for the treatment options. Remedial treatment covers the actual treatment from initial examination to final drying and documentation with a small delay at the beginning for ordering the needed resources as shown in the large yellow bar below. Digitalisation is one of the shortest categories shown in pink. Digitalisation encompasses digitising the photos and saving them in case the originals are lost or damaged in the future. Next up is rehousing as shown in yellow, most of which can be done in any order, barring the first bar which covers ordering required resources which the author mentioned earlier. It leads the final section of the chart shown in the small amount of orange below, to represent setting up the delivery tracking, packaging and insurance application ending in client feedback.
Key Milestones

In the first key milestone, an initial meeting with the client is held to plan the project accordingly and gain a proper perspective of the upcoming project. The second key milestone marks the completion of the planning and treatment proposal that allows the client to give the final check off. The third key milestone is hit after the restoration and/or preservation of the objects completes, along with the treatment and the completion of the following treatment report. The fourth key milestone is digitalisation completed which marks the end of digitalising the photos, in case of future incidents with the existing photos. The fifth key milestone is a small but important milestone that marks the completion in rehousing of the existing photos. The sixth key milestone marks the packaging and shipping reaching its completion, and all left is to wait for the delivery to reach the client. The final milestone simply marks the end of the project.
Budget Allocation & Budget Analysis and Review
| Item | Hours | Cost |
| Documentation | 8 | $ – |
| Digitisation | 2 | $ – |
| Treatment | 30 | $ – |
| Rehousing | 2 | $ – |
| Administration | 2 | $ – |
| Contingency (10%) | 4.4 | $ – |
| Materials used in the treatment | – | $ – |
| Transportation (including insurance and packing) | 0.25 for packing | $ – (plus, parcel shipping & insurance) |
| Polyester sleeves | – | $ – |
| Photo frames | – | $ – |
| Total | $ – |
Here the author just listed the items that need to be cost and estimated hours when planning. The treatment itself will cost the most as it is the main part of this project, it involves the most time and effort, so it must have the highest part of the budget allocation. In each area addressed which has also included the hours involved and factored that in as well for the staff wages. A breakdown like this also helps the project planner to review the budget to see if keeping under.
Record Keeping

There are many documents that the project planner should keep, like project plan and management, quote, treatment proposal, invoice, transaction details, treatment report, risk assessment form, Gantt chart, project checklist, and communication evidence. These should be kept in paper and digital copies.
What Lessons were Learned in this Unit

As the dot points on the slide mentioned that the author had learned from this unit, including this project planning, without adequate planning the planner may screw up the project. In terms of the budget, which needs to know how much exists, any sponsors or external financial support? If not, should the project planner seek more possibilities or scale down the project? In this preservation project, if the client does not have enough money, we can have other treatment options to prioritise the photos which should be treated and how far we treat these photos. Work allocation and communication are the important elements in the project work. How to work and facilitate in a team and how to communicate with stakeholders, the planner should find out the effective approaches to make the project work easier. Use the appropriate tools and channels, which the author thinks are varying and depending on the situations that need to be considered. Additionally, undertaking project work should be aware of communication skills and people’s thoughts. Remember to respect the person you are talking to and proactively listen to their thoughts during the conversation to figure out the best solutions.